The first symptoms usually occur between the ages of 6 and 40, in rare cases also in later adulthood. In children, the focus is usually on elevated liver values and even damage to the liver. In adolescents and young adults, neurological deficits come to the fore.
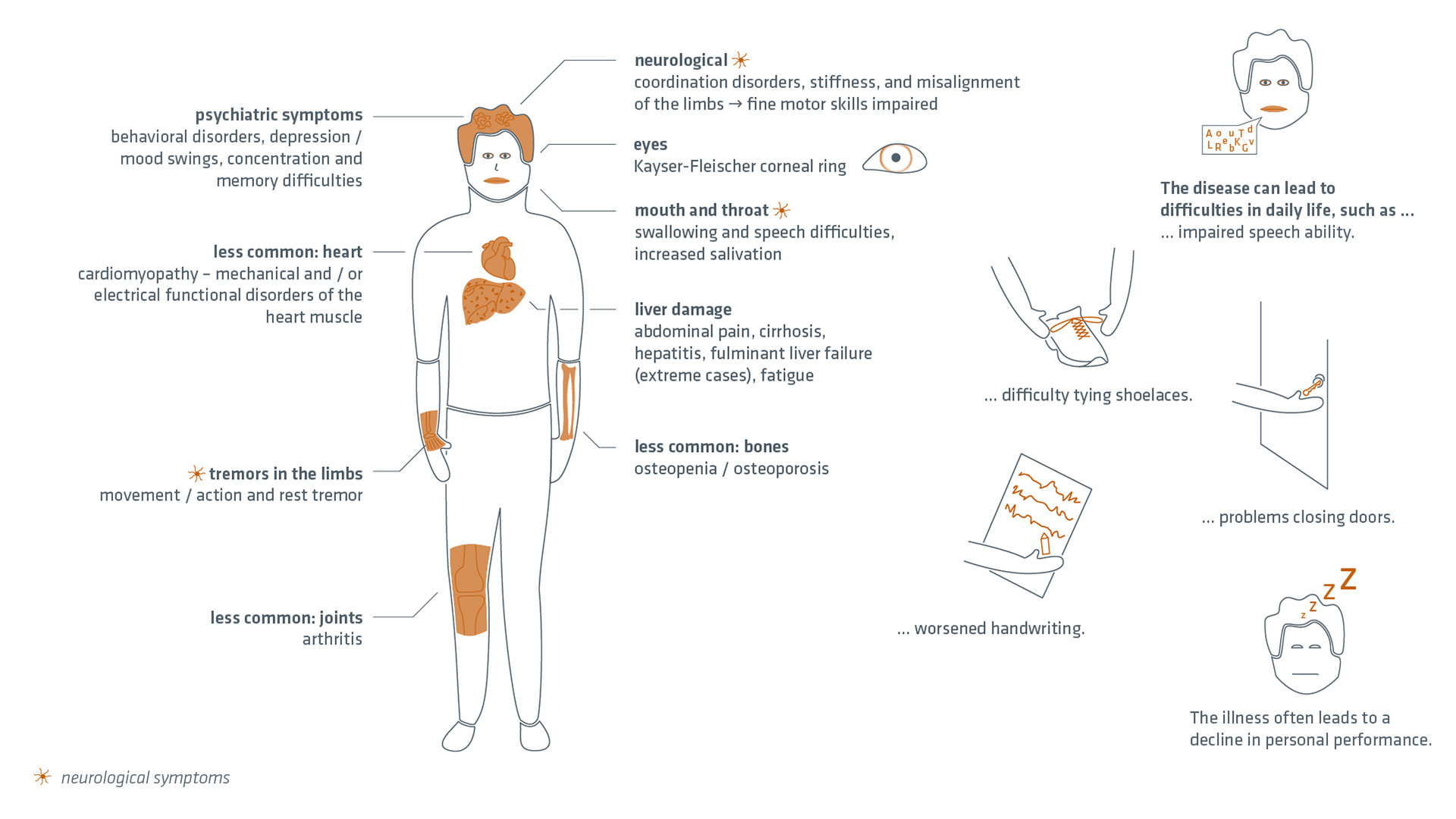
Copper deposits in the eye appear as a greenish-brown coloured ring around the cornea of the eye, the Kayser-Fleischer corneal ring. It is a late rather than an early symptom and is therefore not always found in the early stages.
The symptoms of Wilson's disease can be roughly divided into 2 categories: hepatic and neurological/neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Hepatic symptoms
Classically, mainly hepatic symptoms occur between the ages of 6 and 20. These include, for example:
- general fatigue
- liver cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- stomach and intestinal disorders
- joint pain
- jaundice
- occasionally anaemia
Neurological/neuropsychiatric symptoms
Neurological symptoms often only develop in adulthood between the ages of 20 and 40.
Psychiatric abnormalities range from psychosis and reduced mental capacity to severe behavioural disorders.
Neurologically affected patients have a chance of improvement through drug therapy. However, there are also forms of the disease in which patients have to cope with neurological symptoms for the rest of their lives despite treatment. The extent of the symptoms typically increases with age at diagnosis.
Typical neurological symptoms include, for example:
![]() a deterioration of handwriting
a deterioration of handwriting![]() impaired speech motor skills
impaired speech motor skills![]() trembling of the limbs
trembling of the limbs![]() gait and swallowing disorders
gait and swallowing disorders![]() sometimes also psychological changes
sometimes also psychological changes